Firewall - Traffic Rules
Traffic rules are used to control the flow of incoming and outgoing traffic on a network. These rules specify the conditions under which traffic is allowed or denied, as well as the actions that should be taken when these conditions are met.
For purposes of demonstration we are going to create 4 firewall rules:
-
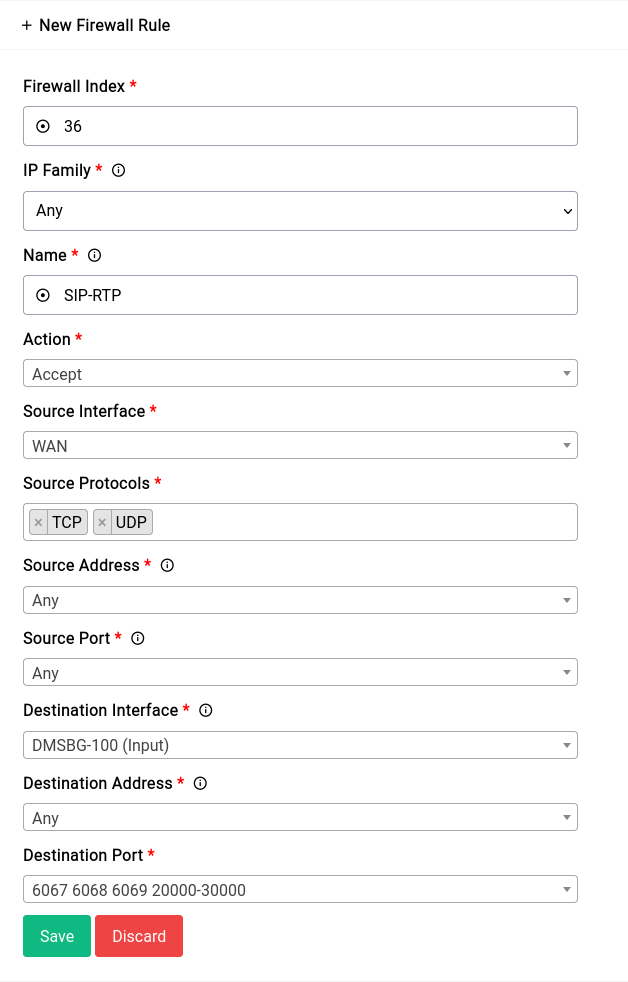
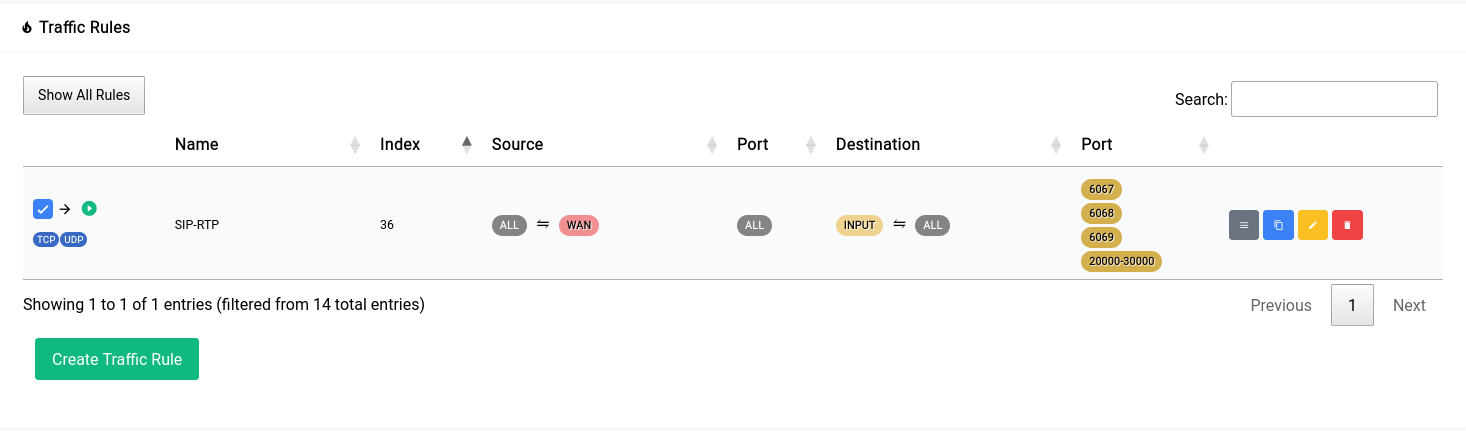
A rule that allows connections to all the SIP and RTP ports which are:
- SIP: 6067 (UDP)
- SIP: 6068 (TCP)
- SIP TLS: 6069 (TCP)
- RTP: 20000-30000 (UDP)
-
A rule that allows for remote administration of Difuse using the TCP ports 80 and 443.
-
A rule that let’s all traffic through to a specific globally routable IPv6 address.
Index’s are assigned automatically at the creation of a new rule. You can edit them later to placed before or after a particular rule if need be using the same index field or you can use the grey button in the table to drag and drop the rules in the order you want.
Allowing SIP and RTP connections
This is what adding the rule should look like:
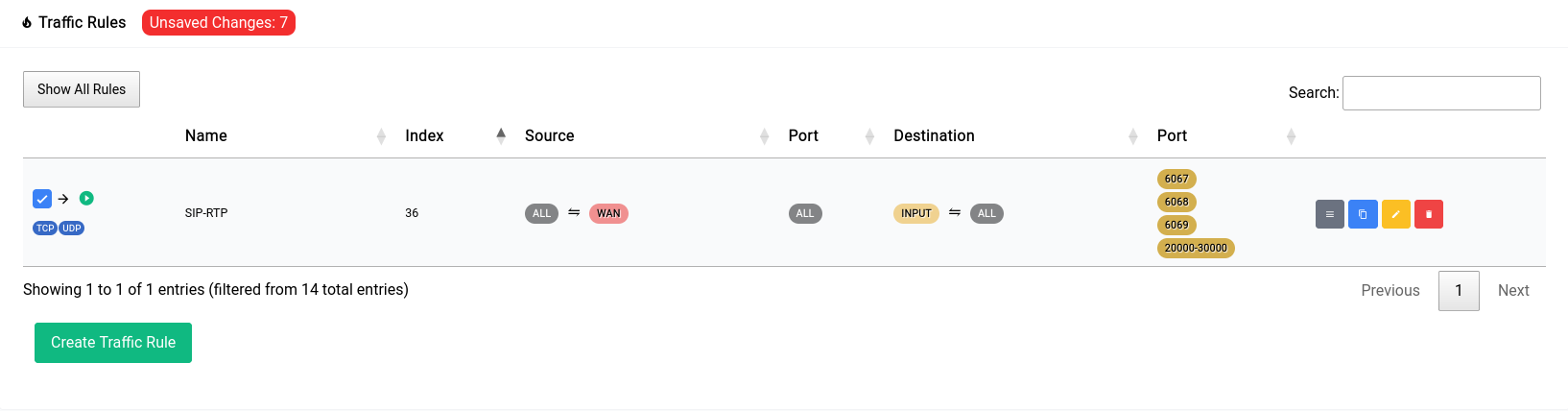
Now once you add a rule, it doesn’t get applied right away. You can see that there’s a red pill that pops up near the title
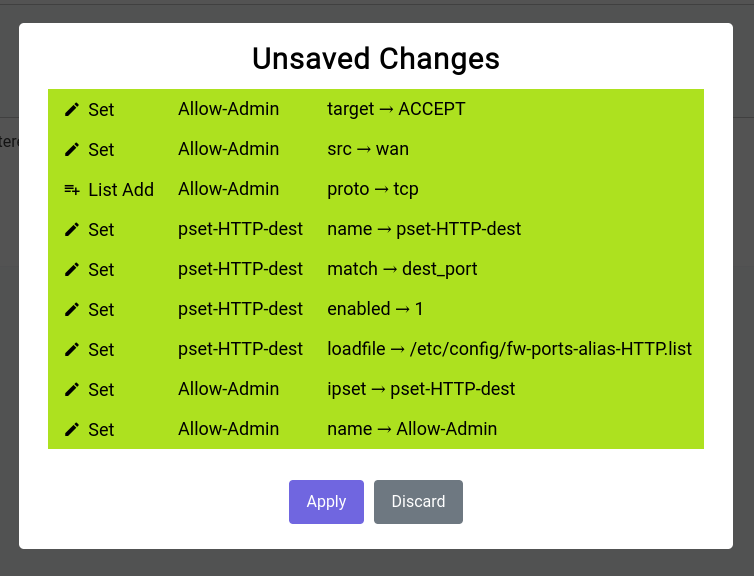
When you click on it, it shows you a gist of the things that have been changed:
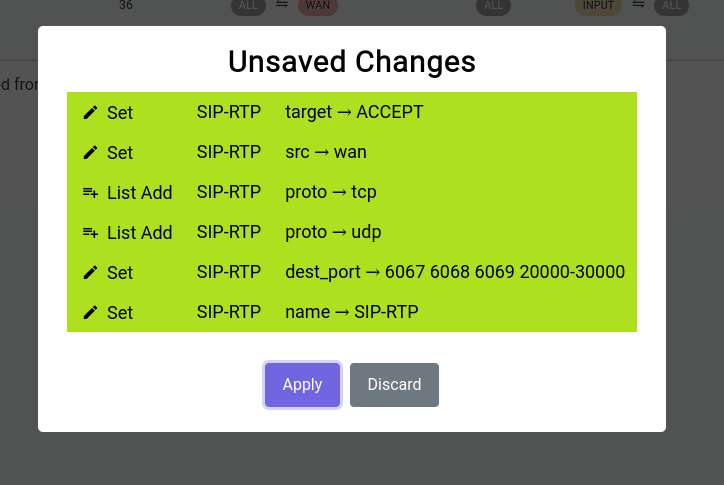
It’s really not a good idea to keep these unsaved changes for a long time as they’re ephemeral and have to be committed to disk or discarded at some point in time.
Once you click apply you will see it go away and the rule you added will show up in the table as such:
Allowing Remote Administration
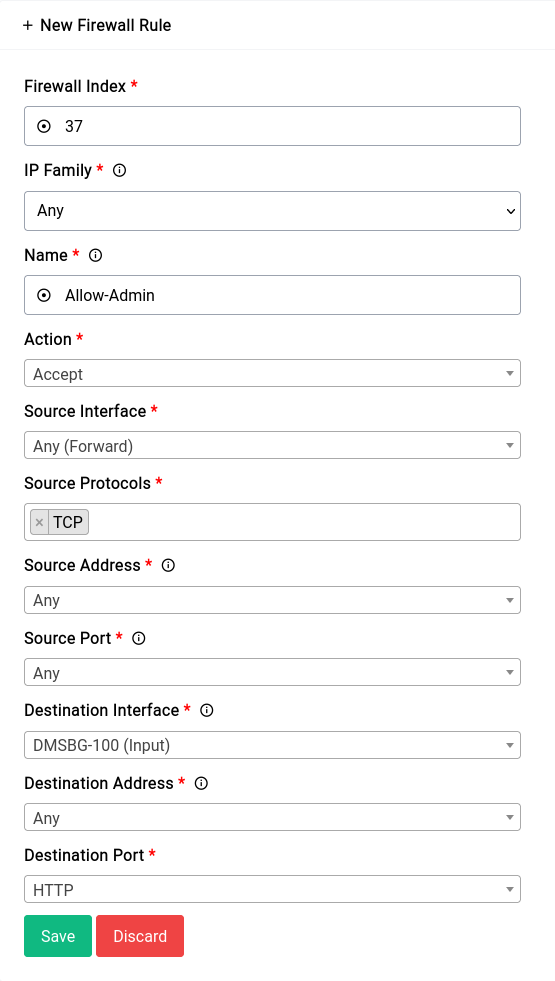
For this rule we’re gonna make use of a Ports Alias. Namely the “HTTP” alias that has the ports 80 and 443 defined. This is just for demonstration you could also just specify the ports directly with a space in between them.
This is an exceedingly bad idea. You should never allow remote administration of your router with source set to ANY ip unless you know what you're doing. We're just using this as an example.
The unsaved changes modal should look something like this:
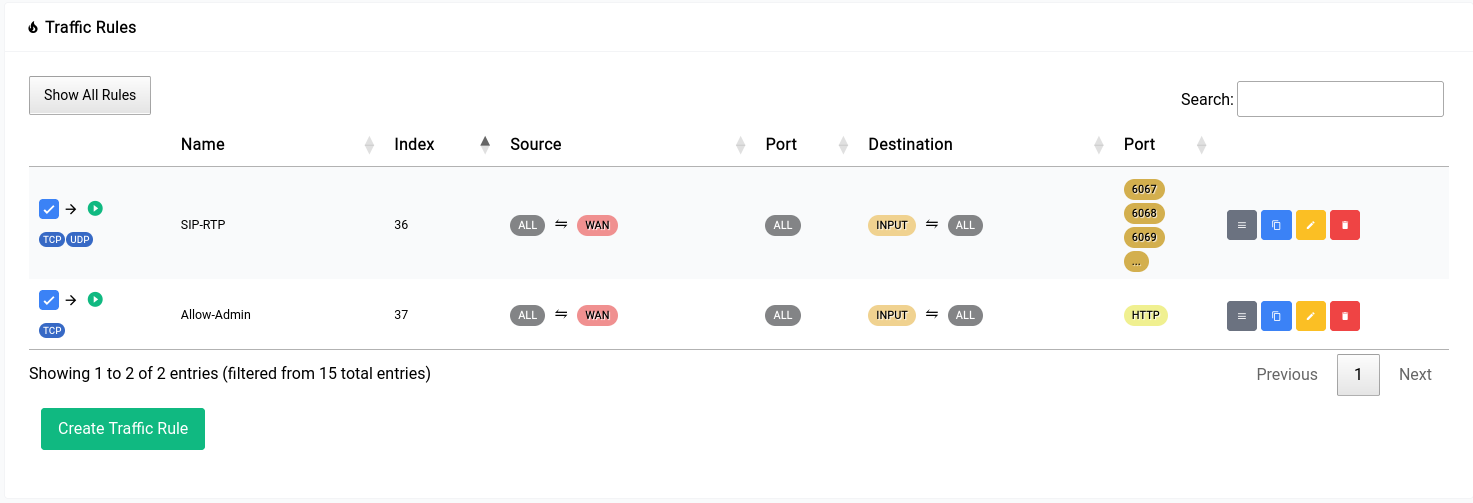
After the rule has been made the table should look something like this:
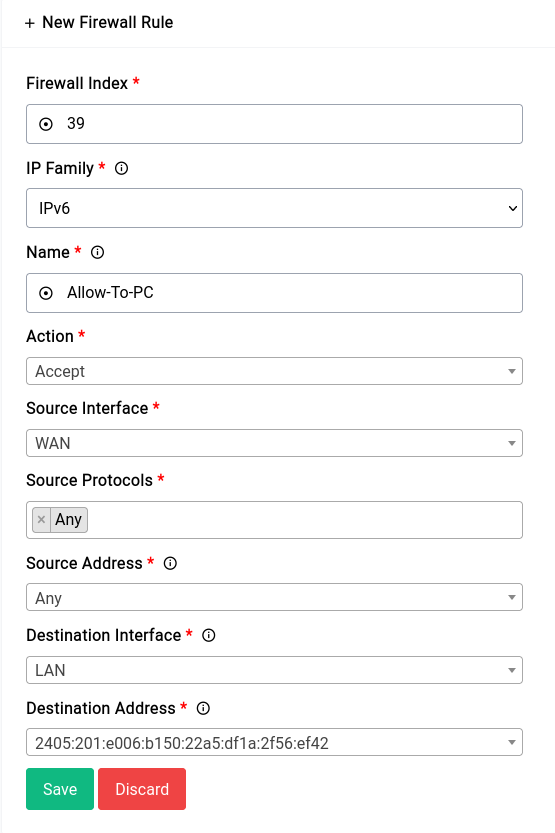
Allowing All Traffic to a Specific IPv6 Address
It's a bad idea to allow all traffic to a specific IPv6 address. You should only do this if you know what you're doing, we're just using this as an example.
If your ISP hands out a sufficiently large prefix (/64 or below) all devices on the host network should already have a globally routable IPv6 address. Now in this case we want the firewall to let all traffic flow to and from a specific IPv6 address without any blocks whatsoever.
First you need to find the IPv6 address of the host and then create a new rule. The new rule would look something like this: